0
- New
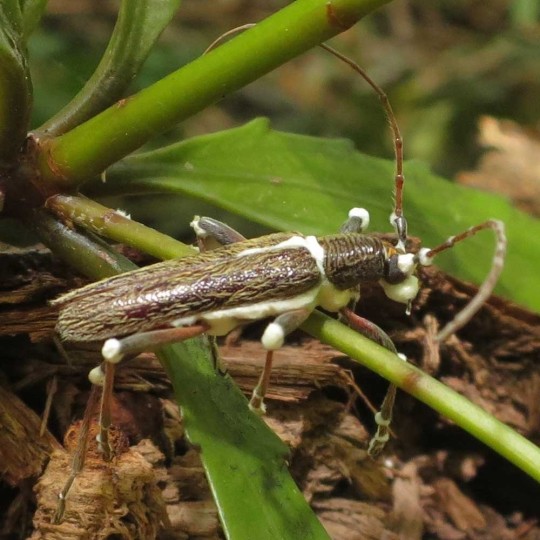
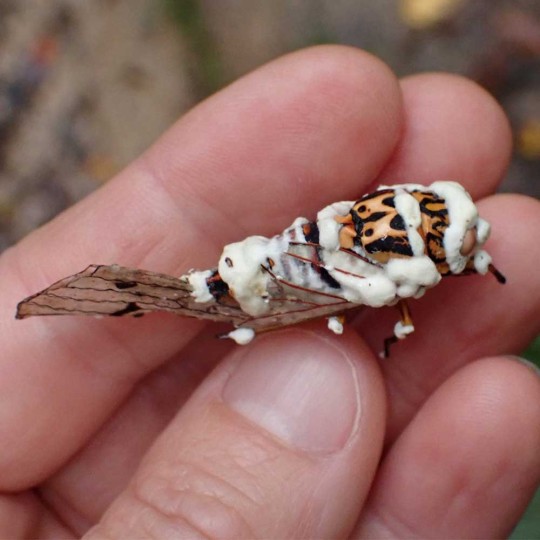
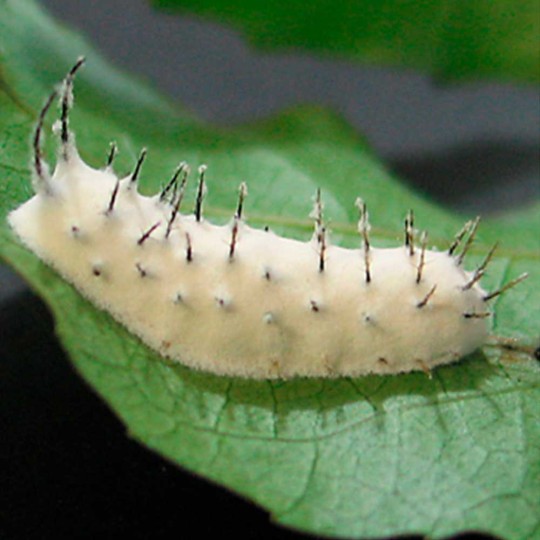
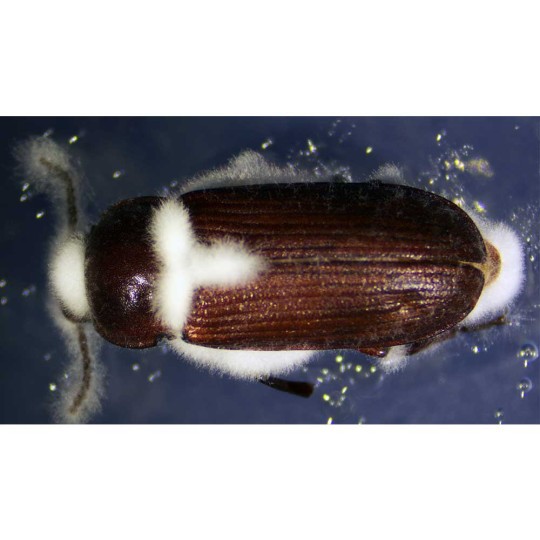
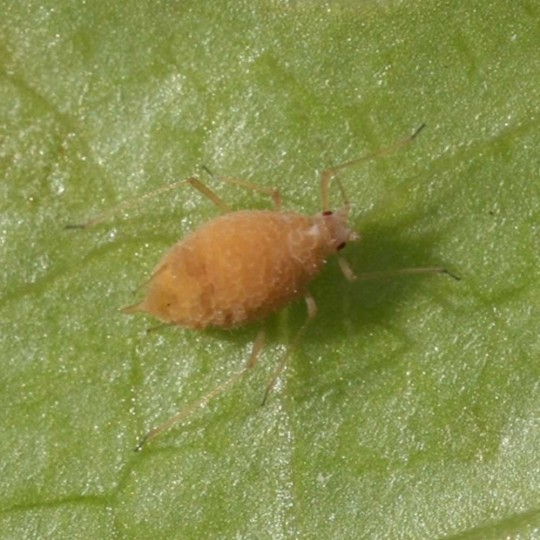




















Natural biopesticide against pest insects (aphids, spider mites, thrips, whiteflies, etc.).
20 grams of powder is enough for 10 liters of water for spraying.
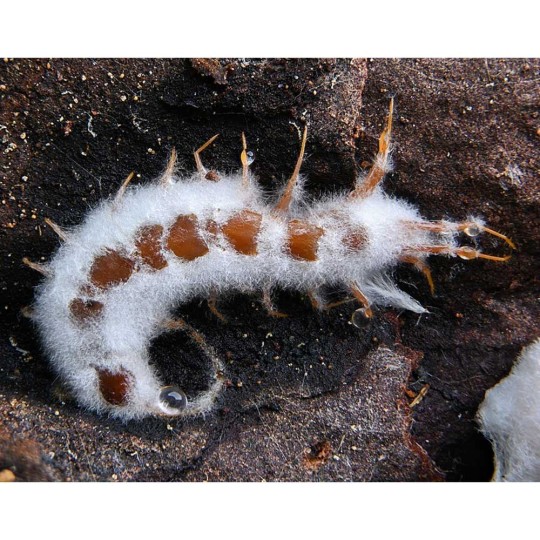
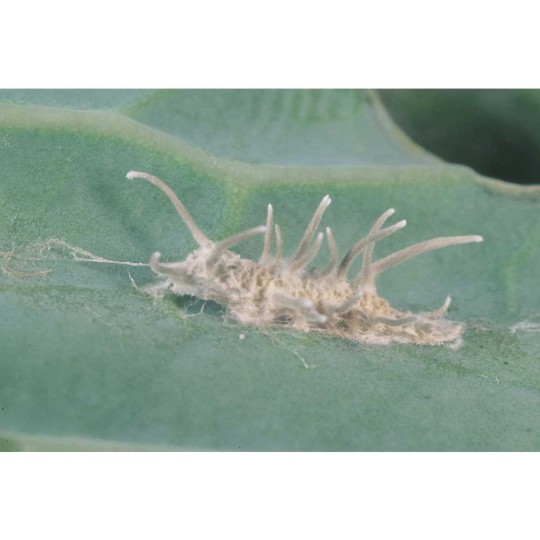
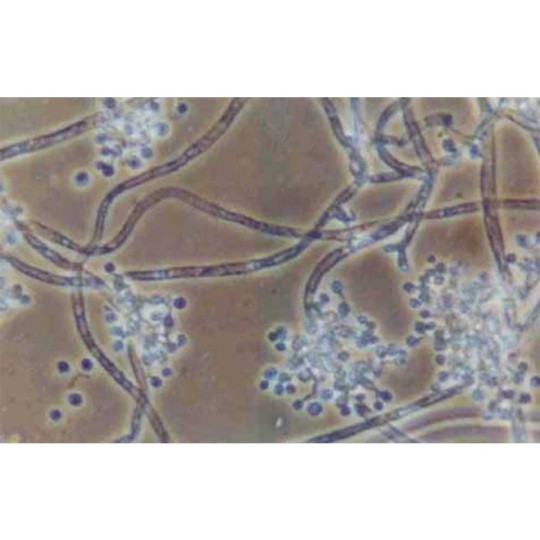
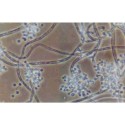
Beauveria bassiana is a non-specific entomopathogen — a parasitic fungus that infects agricultural pest insects and is used to control their populations as a biopesticide.
Spores land on the pest's body surface and germinate into its internal tissues, forming mycelium. Hyphae gradually penetrate the hemolymph, where the fungus actively reproduces and spreads throughout the insect's body. The pathogen consumes nutrients dissolved in the hemolymph and produces toxins. As a result, the host insect dies from exhaustion and intoxication. The mycelium develops and emerges through the integument onto the body surface. Here, spores are formed, which are responsible for infecting the next generation of insects.
Infection occurs in several ways — through direct contact between infected and uninfected individuals, via insect vectors, or through airborne droplets. For example, Beauveria bassiana is effective in killing bed bugs exposed to cotton fabric treated with fungal spores, as infected bugs carry the fungus back to their hiding places.
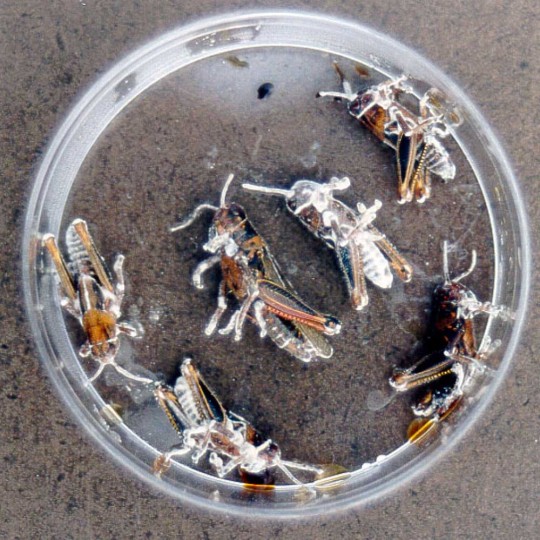
Beauveria bassiana parasitizes a very wide range of arthropods:
Dosage: 2 grams per 1 liter
Spray Beauveria bassiana spores onto affected plants — apply a solution of the powder in water. One package is enough for 10 liters of water.
Safety and Impact on Living Organisms
Beauveria bassiana does not infect plants. Its targets are exclusively insects and other arthropods (mites). It specializes in overcoming their chitinous exoskeleton.